The Ultimate Guide Of Solar Batteries Types
Each solar battery has its own set of advantages and disadvantages in terms of capacity, life-cycle, charge/discharge efficiency, etc. Solar batteries are designed specifically for solar systems rather than vehicle batteries. You might be wondering what the many types of solar batteries are after that.
The four types of batteries available for solar energy storage are as follows:
- Lead-Acid batteries
- Lithium batteries
- Red-ox flow batteries
- Hydrogen batteries
This post will go through solar batteries in detail, including their advantages and disadvantages as well as the many forms available.
Why Do We Need Good Solar Batteries?

Solar batteries are an important part of harnessing solar energy. Solar batteries store the energy collected by solar panels so that they can be used later when there is no sun. This is important because solar panels only generate electricity when the sun shines. Solar batteries allow us to use solar power at night or on cloudy days.
Solar batteries also help to stabilize the grid by providing backup power during peak demand periods or when there is a power outage.
Lastly, solar batteries help us to move towards a more sustainable energy future by eliminating our reliance on fossil fuels.
Overall, solar batteries are a crucial part of the solar energy equation. Without them, we would be unable to harness the sun’s power and use it to meet our energy needs.
What Is A Good Solar Battery?
Solar batteries are constructed to be charged by solar power via a solar charge controller. The ideal solar battery should fulfill the following requirements:
- Tolerant to intermittent solar charging
To properly take advantage of solar power, the battery must be able to tolerate being charged and discharged on an irregular basis. This means that the battery should have a low self-discharge rate to hold a charge for long periods when not in use.
- Durable (high number of charge/discharge cycles, long life)
A good solar battery can withstand many charge and discharge cycles without losing capacity. This is significant because it allows the battery to last for many years, even when used frequently.
- Powerful
The battery should be able to discharge a large amount of power at once to meet the demands of high-powered devices. This is important for things like power tools which may require a sudden burst of energy.
- Accept quick charging/discharging.
Ideally, the battery should be able to be charged and discharged quickly so that you can take advantage of solar power when available. This is important for applications where you need to get the most out of your solar power system.
- Safe
The battery should be safe to use and handle so that you can feel confident using it in your solar power system. This means that the battery should have a low risk of fire and explosion and should not release toxic fumes.
- Robust
Solar batteries are designed to provide a consistent and reliable power supply for the solar panel. The battery should be strong and resilient enough to endure the stress of being used in a solar power system. This implies that the battery may be dropped, banged, or otherwise harmed without failing.
- Compact
Because space is often limited in a solar power system, the battery should be compact to take up as little space as possible. This is important for applications where you need to maximize the use of space, such as in portable solar power systems.
- Lightweight
A good solar battery should be lightweight and easy to transport and install. This is important for applications where you need to be able to move the solar power system, such as in RV or marine applications.
- And ultimately, cheap.
While the price is not the most important factor, it is still important to consider when choosing a solar battery. A good solar battery should be affordable to get the most bang for your buck.
The challenge that scientists and engineers face to bring the best product to market is daunting, but their progress with solar batteries is promising. Let’s investigate the technologies they have developed thus far.
What Kinds of Solar Batteries Are There?
The following four types of solar batteries are available on the market:
- lead-acid,
- lithium batteries,
- red-ox flow and
- hydrogen technologies
Lead-Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries were created in 1857 by Gaston Planté, and they are still the most popular type of rechargeable battery. The main active material in lead-acid batteries is, unsurprisingly, lead. Lead-acid batteries are often compared to lithium-ion batteries, but there are three distinct types of lead batteries that make them a better choice for solar storage:
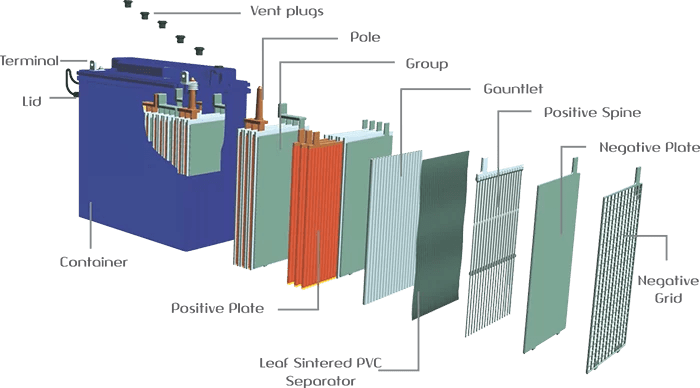
The seal and maintenance-free GEL battery is a sealed, non-disposable battery. It was developed by a German firm more than 70 years ago. The main feature of this solar battery is the gel electrolyte. As a result, there are no gas eruptions or electrolyte leaks under typical usage circumstances.
A gel battery for solar energy has these features:
- Positive electrode: PbO2 (lead oxide)
- Negative electrode: Pb (pure lead)
- Electrolyte: H2SO4 (sulfuric acid as a gel)
- Membrane separator
This battery uses the transfer of H+ ions between the positive and negative electrodes in the electrolyte to operate. This electron flow (electricity) outside the battery is powered by this movement of ions. A solar cell that is connected to a battery will actually cause the charging process to reverse.
In a GEL battery, the electrolyte is in the form of a gel, unlike other lead-acid batteries. This makes the battery virtually spill-proof and much more resistant to vibration damage.
Advantages of GEL batteries:
- No water loss – The electrolyte is in gel form, so there is no water loss due to evaporation.
- Vibration resistant – The gel helps to keep the electrolyte in place, making the battery more resistant to damage from vibrations.
- Long shelf life – A GEL battery can be stored for up to 2 years without recharging.
- Maintenance-free – There is no need to add water to a GEL battery, as there is no water loss due to evaporation.
- Sealed – GEL batteries are sealed, so there is no risk of acid leaks.
- Low self-discharge – GEL batteries have a very low rate, so they can be stored for long periods without losing their charge.
Disadvantages of GEL batteries:
- More expensive – GEL batteries are more expensive than lead-acid batteries.
- Lower capacity – GEL batteries have a lower capacity than lead-acid batteries.
Solar Battery – AGM
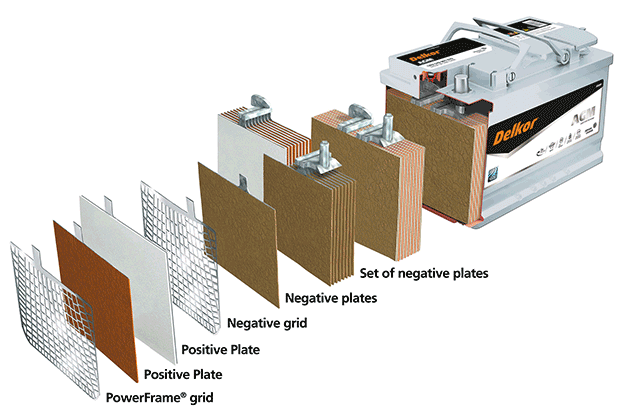
The AGM solar battery is a lead-acid battery invented in the 1980s. “AGM” stands for Absorbed Glass Mat. In this type of battery, the acid electrolyte is absorbed on a glass mat, making it safe and leakproof.
The only difference between this type of battery and a gel battery is that the electrolyte is absorbed onto a fiberglass mat.
This battery functions similarly to a gel battery in that H+ ions generate current flow between the two electrodes. However, the electrolyte in an AGM battery can’t flow freely like in a flooded lead-acid battery. Therefore, it’s important that an AGM battery is installed correctly and that it’s not overcharged or discharged too deeply. AGM batteries offer a longer lifespan and higher performance when used correctly than flooded lead-acid batteries.
Advantages of AGM batteries
- They’re maintenance-free. You don’t have to check the water level or add water to an AGM battery.
- Flooded lead-acid batteries can be installed in any orientation but must be kept upright, so the electrolyte doesn’t spill out.
- They have a higher discharge current. An AGM battery can discharge up to three times more than a flooded lead-acid battery.
- AGM batteries are more powerful for their weight than flooded lead-acid batteries. AGM batteries also have 30% greater capacity despite being lighter.
Disadvantages of AGM batteries
- They cost more than lead-acid batteries filled with water.
- If batteries are discharged too deeply, they will have a shorter lifespan.
Tubular Lead-Acid Batteries –OPzV
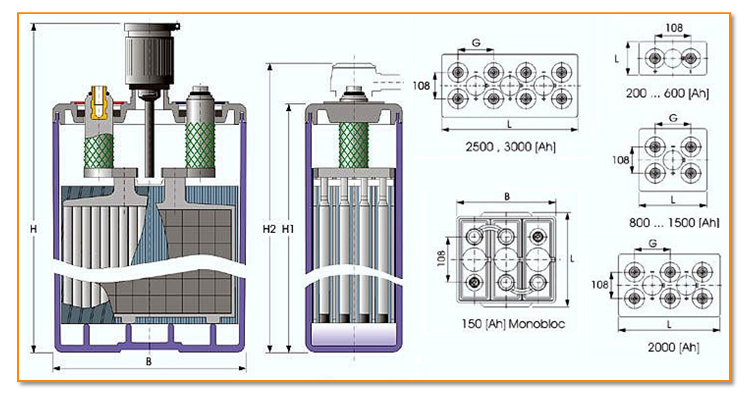
OPzV batteries from the German firm O’ Ortsfest’ (stationary), Pz’ PanZerplatte’ (tubular plate), V Verschlossen, are among the newest additions to the lead-acid solar battery.
AGM, GEL, and OPzV batteries all use tubes as electrodes in order to create a more efficient design for stationary applications. This allows better contact with the acidic electrolyte. Additionally, while OPvZ batteries are sealed and their electrolyte is of gel type, they share enough commonalities with AGM and GEL types that their working principle is virtually the same.
Let’s now take a closer look at how these tubular lead-acid batteries work.
The cells in an OPzV battery are connected in series; when you connect multiple batteries, it creates a string. Strings are then connected in parallel to increase capacity.
As we briefly mentioned before, one of the advantages that OPzV batteries have over other types is that they offer a larger surface area for electrochemical reactions to take place.
This is due to their tubular design; they have a longer service life and higher discharge efficiency.
Regarding charging, two main methods can be used – pulsed or constant current.
- Pulsed charging is where the charge current is interrupted at regular intervals, and this method is often used for deep-cycle batteries.
Constant current charging involves maintaining a steady charge throughout the process, generally used for starter batteries.
- Both methods are effective, but it’s important to note that overcharging can significantly reduce the lifespan of your battery, so it’s important to get the right charger for your needs.
Advantages:
- Longer service life
- Higher discharge efficiency
Disadvantages:
- More expensive than other lead-acid batteries
Lithium Batteries
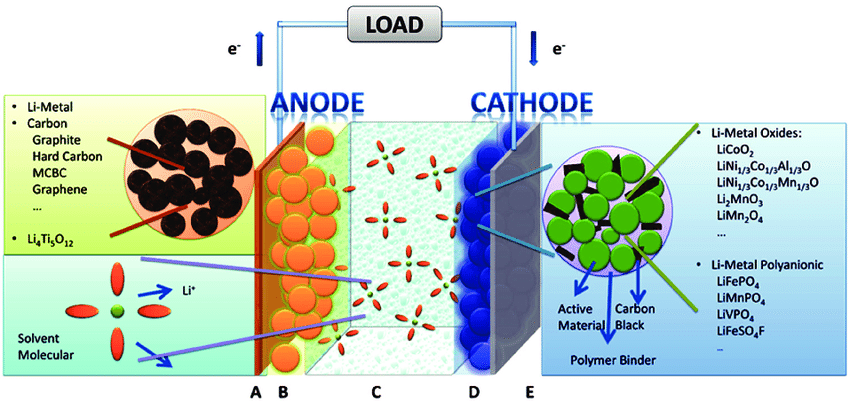
In the 1980s, lithium-ion batteries were invented and became commercially available in the late 1990s. They take advantage of Lithium ions as an ion: Li+ to produce or store electricity. Let’s have a look at the two most common lithium-ion battery technologies:
LiFePo4 Solar Battery
The most popular type of Lithium solar battery on the market today is a LiFePo4 battery. These batteries are typically composed of the following parts:
- Positive electrode: Lithium oxide LiFePo4 (Lithium Iron Phosphate)
- Negative electrode: Carbon
- Electrolyte: lithium salt (Li+, gel type)
- Membrane separator
Using the electrolyte, these batteries employ a mechanism that involves the exchange of lithium ions (Li+) from one electrode to another. This flow of ions generates an outside currently in the battery cell.
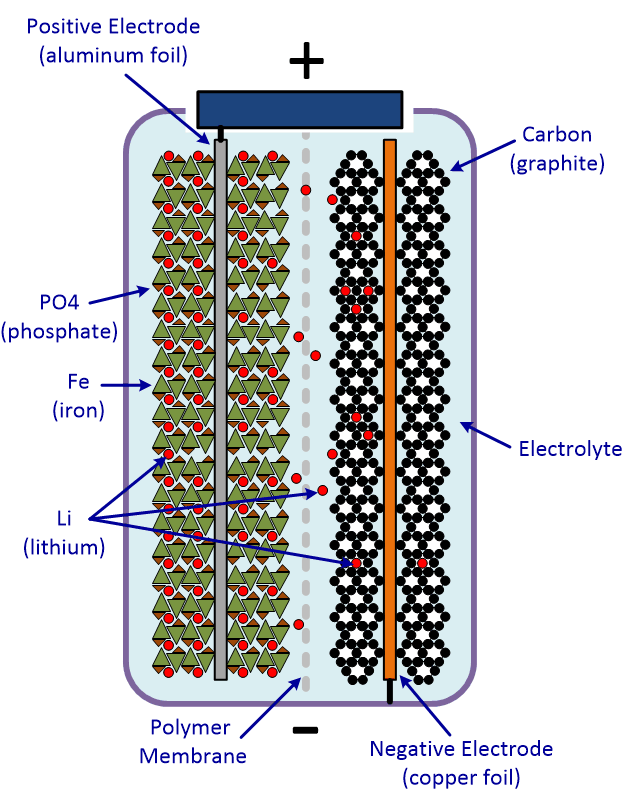
It’s important to remember that, during the charging process, the ions actually flow in the opposite direction than when the battery is discharged.
Advantages of LiFePo4 Batteries
- Lithium-ion batteries are much safer than other types of lithium batteries.
- They’re more resistant to extreme temperatures, both hot and cold.
- Due to their greater charging capability, they can retain a charge for far longer (up to 5 times longer than LiCoO2 batteries).
- Without losing capacity, they can be charged and discharged hundreds of times.
- Lightweight and powerful, these features make our products some of the most sought-after on the market.
Disadvantages of LiFePo4 Batteries
- They’re more expensive than other types of lithium batteries.
- While they boast a longer lifespan, this advantage is offset by their charging times are also longer.
- Their performance in cold weather conditions is not as good as other lithium-ion battery types.
LTO Solar Battery
The third type of lithium-ion solar battery is LTO (Lithium Titanate). It works similarly to LiFePO4 batteries, except for containing different electrode materials.
- The negative electrode (anode): Li2TiO3 (LTO): Lithium Titanate Oxide
- The positive electrode (cathode): lithium manganese oxide
LTO solar batteries are much more resilient (up to 30’000 cycles, 10 years) and effective than other batteries. They have a very low self-discharge rate, making them ideal for storing solar energy. However, they’re also more expensive than other types of lithium-ion batteries.
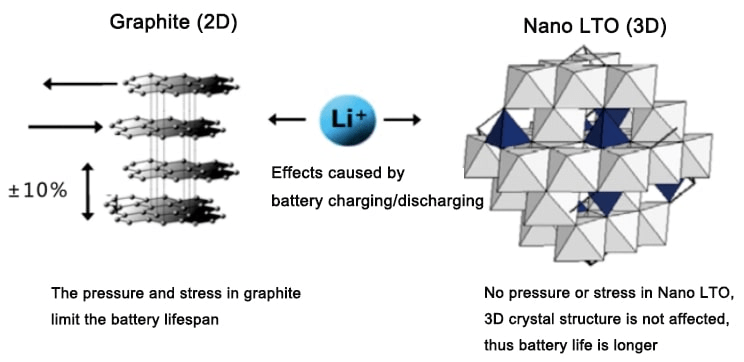
Advantages of LTO Batteries
- They have a very long lifespan (up to 30’000 cycles).
- Unlike traditional lithium-ion batteries, they are more robust and resistant to high temperatures.
- They can be charged and discharged significantly quicker than other types of batteries.
Disadvantages of LTO Batteries
- Not only are they more expensive than other types of lithium-ion batteries, but they’re also more costly.
- Their capacity is lower than that of other battery types.
Vanadium Red-ox flow batteries (VRB)

In the late 1980s, Australian scientists developed vanadium red-ox flow batteries. They’re electrochemical storage systems like other solar batteries. However, their functioning mechanism and components are quite different. The electrolyte in a VRB is flowing, the battery’s primary active component.
A VRB consists of:
- Two tanks of liquid acid electrolytes containing Vanadium ions (V2+)
- Two carbon electrodes
- An Ion exchange membrane
VRB storage capacity is based on the volume of each electrolyte, rather than related to the type of chemical compound used like other batteries. When the electrolytes are in motion, an electrochemical reaction occurs using vanadium ions at the electrodes instead of any other atom or molecule. This way, current is produced outside the battery.
Hydrogen Batteries
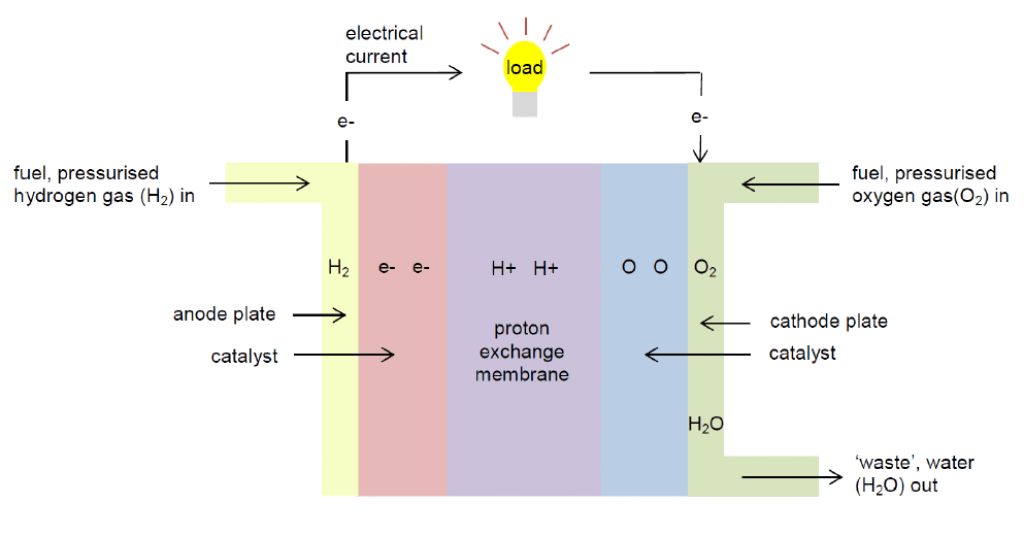
Hydrogen batteries, or hydrogen fuel cells, are a type of energy storage that uses hydrogen and oxygen reactivity.
It consists of a:
- Hydrogen storage tank
- The positive electrode (cathode, graphite)
- The negative electrode (anode, platinum)
- Proton exchange membrane (PEM)
The negative electrode accepts hydrogen as a gas, where it is split into positive ions (H+) and negative electrons (e-) by a platinum catalyst. The PEM membrane then lets the H+ through while the electrons flow outside the system to create an electric current. Meanwhile, water is created as a byproduct when H+ combines with oxygen from the air at the cathode.
Final Thoughts
After doing some research, you’ll notice that there are many types of solar batteries each with its own set of pros and cons. Green ONE Power Tech, a leading supplier of lithium batteries for over 10 years, suggests investigating the different kinds so you can make an informed decision on which one to purchase.
